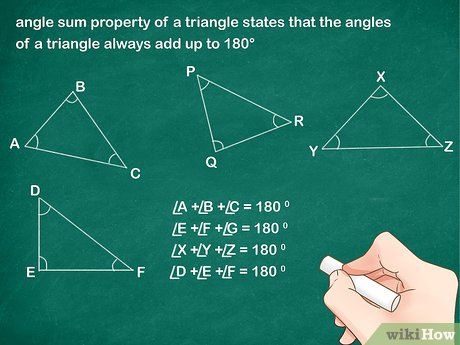
A triangle whose interior angles sum to zero
Spherical geometry In spherical geometry, the interior angles of a triangle add up to more than π. And in fact you can determine the area of a spherical triangle by how much the angle sum exceeds π. On a sphere of radius 1, the area equals the triangle excess Area = E = interior angle sum − π. Small triangles have interior angle sum near π. But you could, for example, have a triangle with three right angles: put a vertex on the north pole and two vertices on the equator 90° longitude apart. Hyperbolic geometry In hyperbolic geometry, the sum of the interior angles of a triangle is always less than π. In a space with curvature −1, the area equals the triangle defect, the difference between π and the angle sum. Area = D = π − interior angle sum. Again small triangles have…


